ASTM A335 P5
Read more
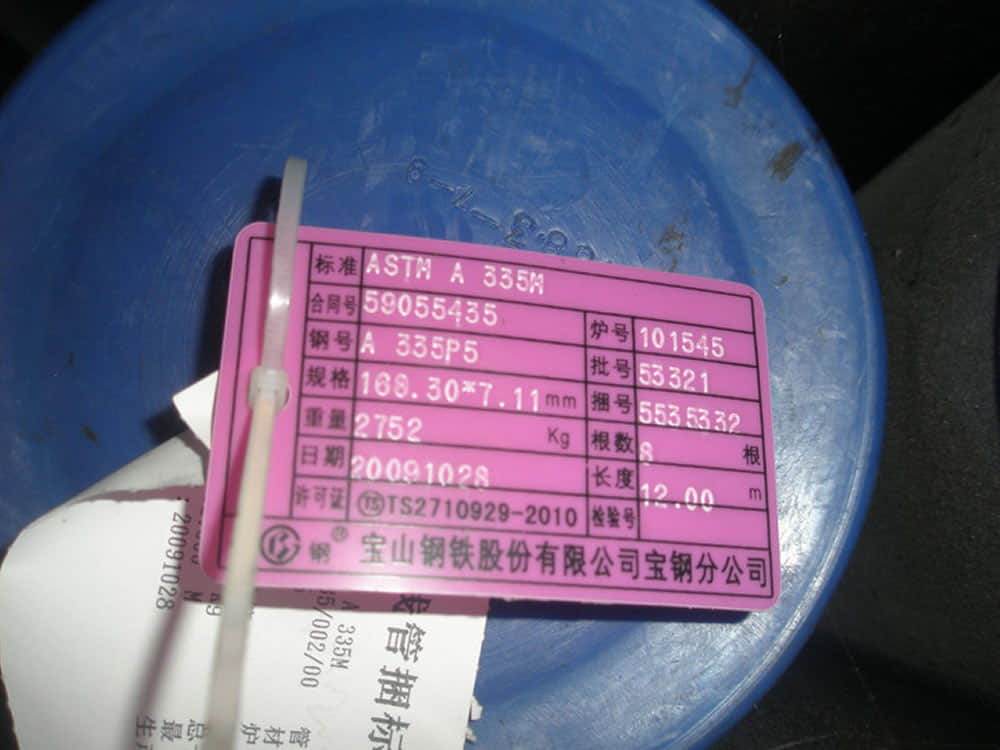
The range of ASTM A335 P5 pipe sizes that may be examined by each method shall be subjected to the limitations in the scope of the respective practice.
These pipes are used in various industries where durability and longevity are crucial.
Download PDF| Spec. | Grade | O.D mm |
W.T mm |
Length mm |
Qty pcs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 25 | 3 | 12000 | 12 |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 32 | 3 | 16 | |
| GB9948 | 1Cr5Mo | 48 | 5 | 8200 | 11 |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 48.3 | 5.08 | 6000-12000 | 83 |
| MAL 037 | 1Cr5Mo | 60.3 | 5 | 6000-12000 | 48 |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 60.3 | 5.6 | 3 | |
| MAL 037 | 1Cr5Mo | 76 | 6 | 6000-12000 | 2 |
| GB9948 | 1Cr5Mo | 89 | 8 | 10000 | 9 |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 101.6 | 5.74 | 10400 | 5 |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 101.6 | 5.74 | 6000-12000 | 4 |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 102 | 8 | 6000-12000 | 3 |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 114.3 | 6 | 11800 | 12 |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 114.3 | 6 | 6000-12000 | 5 |
| GB9948 | 1Cr5Mo | 114 | 7 | 6000-12000 | 9 |
| GB9948 | 1Cr5Mo | 114 | 8 | 8000 | 16 |
| GB9948 | 1Cr5Mo | 114.3 | 8.56 | 6000-12000 | 42 |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 152 | 6.5 | 11000 | 4 |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 152 | 6.5 | 6000-12000 | 2 |
| GB9948 | 1Cr5Mo | 152 | 8 | 6000-12000 | 5 |
| JIS G3467 | STFA25 | 152.4 | 10 | 12000 | 53 |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 159 | 8 | 2 | |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 159 | 8 | ||
| GB9948 | 1CR5MO | 168 | 6 | 6000-12000 | 13 |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 168 | 7 | 6000-12000 | 13 |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 168.3 | 7.11 | 12000 | 44 |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 168.3 | 7.11 | 6000-12000 | 7 |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 168.3 | 7.11 | 28/259.85,20/166.28 | 58 |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 168.3 | 7.11 | 12000 | 57 |
| GB9948 | 1CR5MO | 168 | 9.5 | 28 | |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 168.3 | 10.97 | ||
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 168.3 | 14.27 | 37 | |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 168.3 | 16 | 22 | |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 168.3 | 24 | 5000 | 2 |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 219.1 | 8 | ||
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 219.1 | 8.18 | 6000 | 24 |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 219.1 | 8.18 | 12000 | 37 |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 219.1 | 10 | 9600 | 35 |
| GB9948 | 1CR5MO | 219 | 10 | 24 | |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 219.1 | 12 | 10 | |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 219.1 | 14 | ||
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 219.1 | 16 | ||
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 219.1 | 18 | ||
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 219.1 | 20 | 11 | |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 219.1 | 24 | ||
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 273 | 9 | 3 | |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 273.1 | 9.27 | 14 | |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 273.1 | 10 | 15 | |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 273.1 | 15.09 | 9 | |
| GB9948 | 1CR5MO | 273 | 18 | 2 | |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 323.9 | 10.31 | 12000 | 10 |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 325 | 12 | 2 | |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 355.6 | 27.79 | 8000 | 4 |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 377 | 15 | 1 | |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 377 | 16 | 11 | |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 406 | 14 | 3 | |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 406.4 | 26.19 | 7000 | 5 |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 406.4 | 30.96 | 6000 | 6 |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 473 | 14 | 2 | |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 609.6 | 16 | 1 | |
| ASTM A335 | P5 | 914 | 32 | 1 |
Our team of experienced sales specialists proudly partners with gas and chemical processors, power generation plants, oil refineries, and related industries to offer piping components and value-added services.
Alloy steels are made by combining carbon steel with one or several alloying elements, such as manganese, silicon, nickel, titanium, copper, chromium and aluminum. These metals are added to produce specific properties that are not found in regular carbon steel. The elements are added in varying proportions (or combinations) making the material take on different aspects such as increased hardness, increased corrosion resistance, increased strength, improved formability (ductility); the weldability can also change.
Commonly used alloying elements and their effects are listed in the table given below.
| Alloying Elements | Effect on the Properties |
|---|---|
| Chromium | Increases Resistance to corrosion and oxidation. Increases hardenability and wear resistance. Increases high temperature strength. |
| Nickel | Increases hardenability. Improves toughness. Increases impact strength at low temperatures. |
| Molybdenum | Increases hardenability, high temperature hardness, and wear resistance. Enhances the effects of other alloying elements. Eliminate temper brittleness in steels. Increases high temperature strength. |
| Manganese | Increases hardenability. Combines with sulfur to reduce its adverse effects. |
| Vanadium | Increases hardenability, high temperature hardness, and wear resistance. Improves fatigue resistance. |
| Titanium | Strongest carbide former. Added to stainless steel to prevent precipitation of chromium carbide. |
| Silicon | Removes oxygen in steel making. Improves toughness. Increases hardness ability |
| Boron | Increases hardenability. Produces fine grain size. |
| Aluminum | Forms nitride in nitriding steels. Produces fine grain size in casting. Removes oxygen in steel melting. |
| Cobalt | Increases heat and wear resistance. |
| Tungsten | Increases hardness at elevated temperatures. Refines grain size. |

When you partner with Sunny Steel, you can stop worrying about meeting deadlines thanks to our responsive and timely service. You'll also say goodbye to unnecessary shopping around. Instead, you'll get white glove service from an expert who understands your needs and can get you the materials you need quickly.
